CiteScore is journal metric launched by Elsevier in December 2016, to give a more comprehensive, transparent and current view of a journal's impact. CiteScore metrics are part of the Scopus basket of journal metrics that include SNIP (Source Normalized Impact Per Paper), SJR (SCImago Journal Rank), citation -and document- counts and percentage cited, providing insights into citation impact for over 22,000 titles.
CiteScore Metrics are a family of eight complementary indicators listed below. You can find out more about the individual indicators on the Scopus Journal Metrics website.
- CiteScore
- CiteScore Tracker
- CiteScore Percentile
- CiteScore Quartiles
- CiteScore Rank
- Citation Count
- Document Count
- Percentage Cited
Calculation
| CiteScore = | No. of Citations to document during previous 4 years |
| No. of Published Documents during previous 4 years (Articles, reviews, or notes that are citable) |
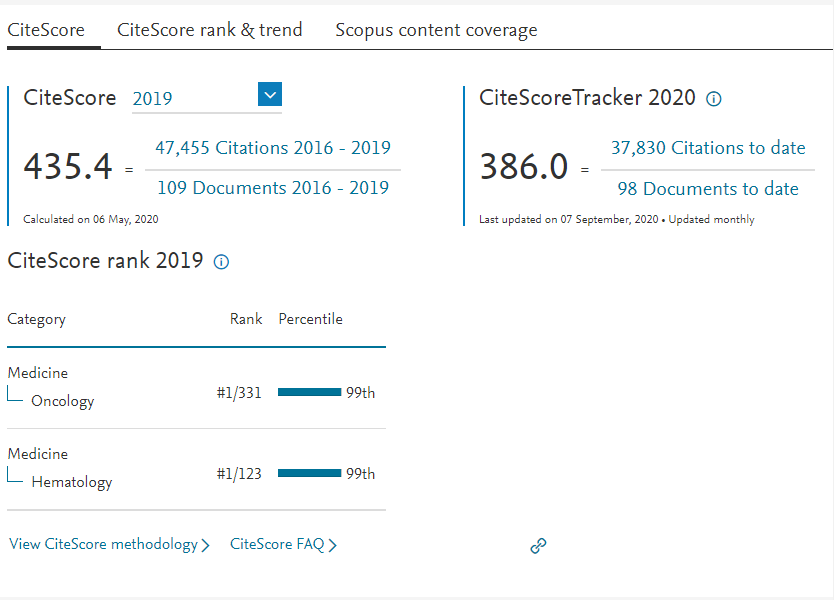
Example: Calculation of CiteScore in the Year 2019:
- Total No. of Citations during 2016 and 2019. (Example A = 47,455)
- Total No. of Published Documents (include articles, reviews, or notes that are citable) during 2016 and 2019). (Example: 109)
47455⁄109 = 435.4
Meaning articles in a journal published during the past 4 years, have been cited 435.4 times in average in 2019.
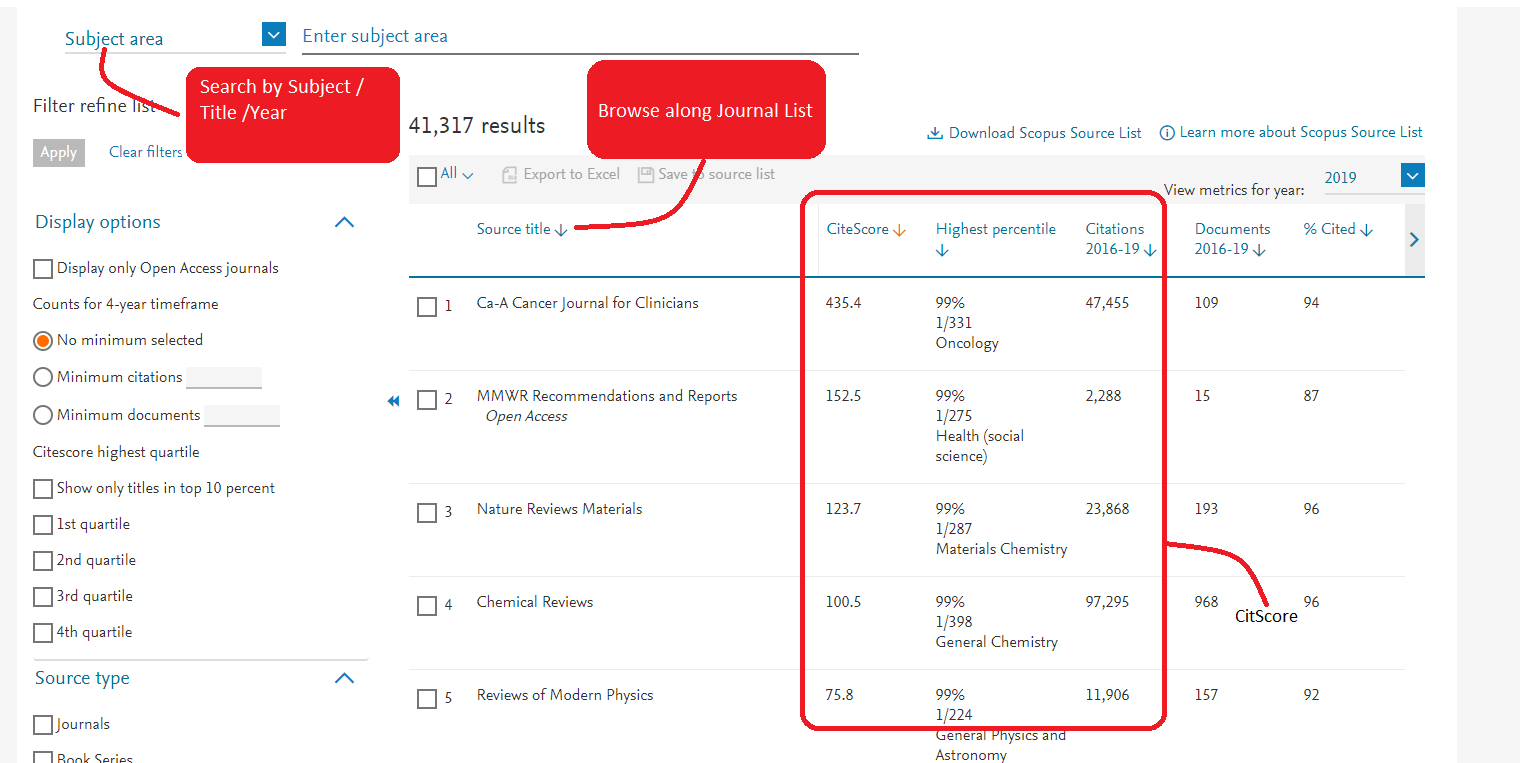
Go to: Scopus Journal Metrics website, you can get CiteScore a particular journal title by
- Search by Subject / Title / Year
- Browse along Journal List
Points to Note about CiteScore
- Cannot be used to compare journals across different disciplines
- May assign journal in more than 1 subject discipline. For journals being assigned in multiple disciplines, the CiteScore Percentile will use the one where that journal being ranked the highest

